In the world of international transportation and trade, there are numerous terms that can cause confusion. Two commonly misunderstood terms are “Transit” and “Transshipment.” While both concepts are related to the movement of goods between countries, they have significant differences. In this article, we will explore the differences between transit and transshipment, the steps involved in each, and their applications, so that traders and supply chain managers can fully understand these concepts.
1. Definition of Transit
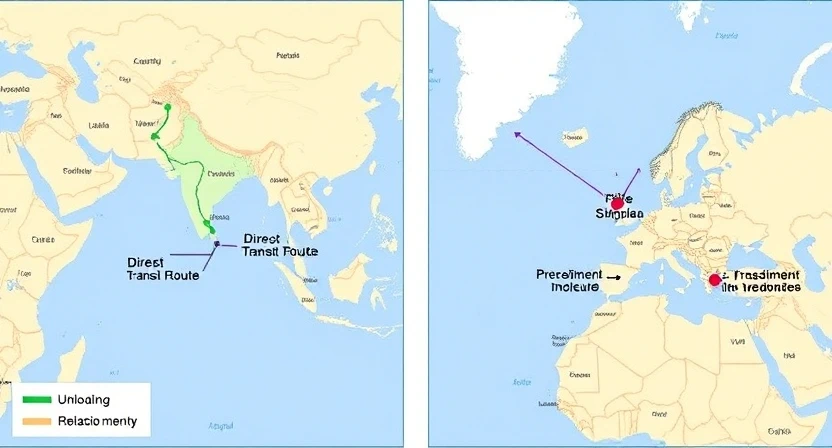
Transit refers to the process in which goods are transferred from one country to another without entering the consumer market of the intermediary country. In this case, the goods only pass through the transit route to reach their final destination. Transit is usually carried out when the intermediary country serves as a shorter and more economical route for transporting goods to the final destination.
In transit, goods pass through specific routes without the need for unloading or changing the means of transportation.

2. Definition of Transshipment
Transshipment refers to the unloading and reloading of goods during the transportation route. This process occurs when goods need to be transferred from one means of transportation to another to reach their final destination. Transshipment is mostly used in maritime and air transportation, especially when there is no direct route for the movement of goods, and a change in the means of transportation is required at an intermediate port or airport.
Transshipment can be used for reasons such as reducing transportation costs, port limitations, or the absence of a direct route for moving goods.

3. Key Differences Between Transit and Transshipment
- Mode of Goods Transfer: In transit, goods pass through the intermediary country without unloading and reloading, while in transshipment, goods need to be unloaded, reloaded, and transferred to another means of transportation.
- Type of Transportation: Transit is usually conducted in land and rail transportation, while transshipment occurs more in maritime and air transportation.
- Duration: Typically, transshipment takes more time than transit due to the need for unloading and reloading.
- Regulations and Permits: Both transit and transshipment require specific permits, but the regulations related to transshipment, especially in ports, are more complex.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Transit and Transshipment
Advantages of Transit
- Reduced transportation costs due to no need for unloading and reloading.
- Faster delivery of goods to the final destination.
Disadvantages of Transit
- The need to use specific routes, which may create limitations for route selection.
Advantages of Transshipment
- The possibility of using various combinations of transportation to reach the destination.
- Greater flexibility in choosing the route and means of transportation.
Disadvantages of Transshipment
- Increased costs associated with unloading and reloading.
- Increased transportation time due to the need for stopping and changing the means of transport.

5. Applications of Transit and Transshipment
Transit and transshipment are both used in specific situations. Transit is mainly used for goods that need to pass from one country to another without unloading, such as goods transferred from Central Asia to Europe. On the other hand, transshipment is used when direct transfer of goods to the final destination is not possible, such as when sea freight requires changing ships at a port.

6. Challenges of Transit and Transshipment
Both transit and transshipment methods come with challenges. Some of these challenges include:
- Customs Issues: Transit and transshipment goods may require complex customs inspections, which can cause delays in transportation.
- Infrastructure Limitations: The lack of proper infrastructure for unloading and reloading in ports can lead to issues in transshipment.
- Security Risks: Both methods may face security risks such as theft or damage to goods, especially at border points or ports.

Conclusion
Understanding the differences between transit and transshipment helps traders and supply chain managers choose the best method for moving their goods. Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, and depending on the type of goods, destination, and available infrastructure, one may be more suitable. Considering specific needs and conditions, traders can optimize transportation costs and time by making the right choice between transit and transshipment.